In computer programming, "operator" is used for perform operations between operands known as operator. Basically there are three types, unary operator , binary operator and ternary operator. In unary operator , we use single operand like (a++,a--), in binary operator we use two operands like ( a+b) and in ternary operator we use three operands like a>b?a:b
int a=10;
Here, variable a is initialized with value 10. It means you can say the right hand side value is copy to left hand side variable using assignment operator.
Int firstnumber=10;
Bool result;
Result = firstnumber>10? True: false;
In the preceding example, if condition becomes true or you can say if firstnumber is greater than to 10 then ternary operator gives ‘true’ in results otherwise gives ‘false’. 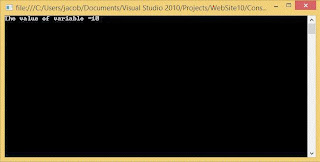 Here, condition if check equality operation between operands, a and constant value 10. If condition becomes true, output comes "The value of variable=10".
Here, condition if check equality operation between operands, a and constant value 10. If condition becomes true, output comes "The value of variable=10".
Assignment Operator (=)
if we create a variable of type integer also we want to initialize it with some value then we should use assignment operator like.int a=10;
Here, variable a is initialized with value 10. It means you can say the right hand side value is copy to left hand side variable using assignment operator.
Arithmetic Operators ( +,-,*,/,%)
Basically arithmetic operators are used for doing mathematical calculation like addition of two or more numbers , multiplication, division, subtraction, and remainder. lets take a simple example to understand arithmetic operators. If the total collection by five students is five thousand then find the average value?.
int collected_money=5000;
int total_student =5;
int avg=collected_money/total_student;
Ternary operator (?, : )
In ternary operator we have three operands, in which first operand is used for check the condition and other two operands is used for giving results. Let’s take a simple example to understand the ternary operator.
Int firstnumber=10;
Bool result;
Result = firstnumber>10? True: false;
In the preceding example, if condition becomes true or you can say if firstnumber is greater than to 10 then ternary operator gives ‘true’ in results otherwise gives ‘false’.
Comparison Operators (< , > ,<=,>=,!=,==)
using comparison operator you can perform Boolean operation between operands known as comparison operator. Lets take an simple to understand comparison operator
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
if (a==10)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("The value of variable ={0}", a));
}
Console .ReadKey (false);
}
}
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
if (a==10)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("The value of variable ={0}", a));
}
Console .ReadKey (false);
}
}
 Here, condition if check equality operation between operands, a and constant value 10. If condition becomes true, output comes "The value of variable=10".
Here, condition if check equality operation between operands, a and constant value 10. If condition becomes true, output comes "The value of variable=10".Logical operator (&&,|| )
Perform logical operation between Boolean operands known as logical operator. Lets take a simple example
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a = true;
bool b = true;
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a = true;
bool b = true;
if (a&&b)
{
Console.WriteLine("condition becomes true");
}
Console .ReadKey (false);
}
}
{
Console.WriteLine("condition becomes true");
}
Console .ReadKey (false);
}
}
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar