Introduction
In this example we will learn about BackgroundWorker control with their properties and events. Background worker is normally used where you want to run some operations on separate thread. As the name indicate "BackgroundWorker" means you can run your background thread simultaneously with your Application.
Some useful Public Properties of Background worker class are:
WorkerReportsProgress : you can retrieve or set the value in WorkerReportProgress. That value indicates whether the BackgroundWorker can report progress updates. This property is capable of indicating to the rest of the application as well as executes.
WorkerSupportsCancellation : You can cancel your update asynchronously using set true to WorkerSupportCancellation property.
Lets take an simple example
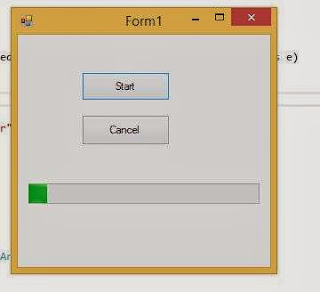
Step-1 : Add some controls (two button control, one progress Bar and one Background Worker control) on forms.
Step-2 : Set both WorkerReportProgress and WorkerSupportCancellation property to true.
Step-3 : Handle some events (Button_click, backgroundWorker1_DoWork, ProgressChanged, RunWorkerCompleted) which are related to Button and BackgroundWorker.
Step-4 : Write the below code in .cs file
Step-4 : Write the below code in .cs file
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
int count = (int)e.Argument;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=count; i++)
{
if (backgroundWorker1.CancellationPending)
{
e.Cancel = true;
break;
}
sum += i;
backgroundWorker1.ReportProgress(i * 100 / count);
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
}
e.Result = sum;
}
private void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgse)
{
progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage;
}
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgse)
{
progressBar1.Value = 0;
if (e.Cancelled)
{
MessageBox.Show("Cancel BackGroundWorker");
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Result:" + e.Result);
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(100);
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
progressBar1.Value = 0;
backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync();
}
}
}
Learn code in detail
Now RunWorkerAsync is the method of BackgroundWorker compound directly call to DoWork event handler with 100 integer argument. In DoWork event handler count variable contains 100. Every iteration in "for" loop will check whether CancellationPending property is true or false (by-default) that means whether your cancel button is pressed or not. If your cancel button is pressed then CancelAsync() method of the BackgroundWorker will run and Your CancellationPending property is set to true.



Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar