Introduction
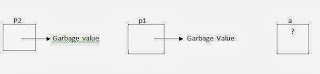
Definition : It is possible to make a pointer to point to another pointer variable. A variable which contains address of a pointer variable is called pointer to a pointer. For example, consider the following declarations:int a;
int *p1;
int *p2;
- The first declaration instructs the compiler to allocate the memory for the variable a in which integer data can be stored.
- The second declaration tells the compiler to allocate a memory for the variable p1 in which address of an integer variable can be stored.
- The third declaration tells the compiler to allocate a memory for the variable p2 in which address of a pointer variable which points to an integer can be stored. The memory organization for the above three declaration is shown below:
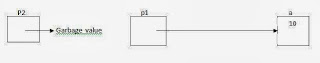
Example: Memory organization after executing following assignment statement:
a=10;
p1=&a;
p2=&p1;
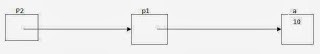
The data item 10 can be accessed using three variables a, p1 and p2 as shown below:
a refers to the data item 10
*p1 Also refers to the data item 10. Here, using p1 and only one indirection operator, the data item 10 can be accessed.
**p2 Also refers to the data item 10. Here, using p2 and two indirection operators the data item 10 can be accessed (i.e., *p2 refers to p1 and **p2 refers to a)

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar