After binding records with DataGridView, there may be some options to edit or to remove those records. To do these simple task we can provide either a button, which gets the selected record and perform operation, or we can provide the button with each particular record.
We will discuss here how to add a button with particular record with the following simple steps. Drag-n-drop a datagridview on the form and a task pop-up menu will automatically open, click on Add Columns link button to add a new column. It will show following Add Column window.
By default Unbound column radio button have been checked, if not check it and use the following values in respective fields:
To write text on the button generate Cell_Formatting event of dataGridview and set the value of first column as I do in the following c# code:
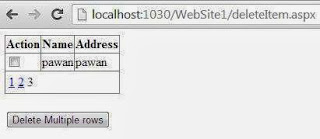
When you run the project now, it will show “remove” on the button. To check if this code will works for multiple records or not, add some records in data gridview like How to add Records in Datagridview. Run the project now and it will show the Remove button with each record as shown in the following image:
In the next article I will remove the particular record with this command button.
We will discuss here how to add a button with particular record with the following simple steps. Drag-n-drop a datagridview on the form and a task pop-up menu will automatically open, click on Add Columns link button to add a new column. It will show following Add Column window.
By default Unbound column radio button have been checked, if not check it and use the following values in respective fields:
- Type: DataGridViewButtonColumn
- Header Text: Command (Changeable)
To write text on the button generate Cell_Formatting event of dataGridview and set the value of first column as I do in the following c# code:
private void dataGridView1_CellFormatting(object sender, DataGridViewCellFormattingEventArgs e)
{
dataGridView1.Rows[e.RowIndex].Cells[0].Value = "Remove";
}
{
dataGridView1.Rows[e.RowIndex].Cells[0].Value = "Remove";
}
When you run the project now, it will show “remove” on the button. To check if this code will works for multiple records or not, add some records in data gridview like How to add Records in Datagridview. Run the project now and it will show the Remove button with each record as shown in the following image:
In the next article I will remove the particular record with this command button.